 |
 |
 ERS (European Remote Sensing Satellite), European Space Agency
ERS (European Remote Sensing Satellite), European Space Agency
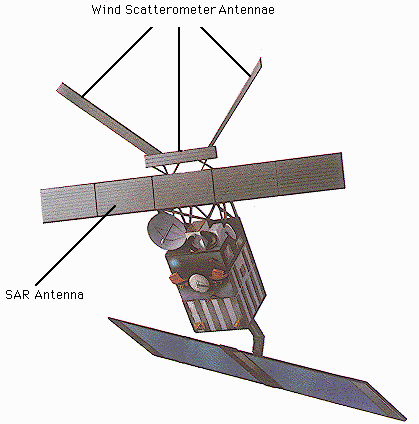 The ERS-1, 2 satellites are intended for global measurements of sea wind and waves, ocean and ice monitoring, coastal studies and land sensing using active and passive microwave remote sensing systems. ERS-1 was launched in July 1991 and ERS-2 in April 1995. ERS-1 uses a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) instrument to acquire images of ocean, ice and land regardless of cloud and sunlight conditions. Other microwave instruments measure sea state, sea surface winds, ocean circulation, sea and ice levels, as well as the sea's surface temperature. The near polar sun-synchronous orbit of the satellite enables a global mission providing world-wide geographical and repetitive coverage, primarily oriented towards ocean and ice monitoring, but with an all-weather high resolution microwave imaging capability over land and coastal zones. ERS-2 is practically identical to ERS-1, with the addition of the GOME sensor for global ozone monitoring. The orbits of ERS-1 and 2 are such that ERS-2 follows the same ground track as ERS-1, except for a 1-day delay. This provides an opportunity to obtain tandem interferometric data of an area using the synthetic aperture radar on the two satellites. The tandem data has better coherence property than the data obtained from 35-day repeat passes of a single satellite. The tandem mission was operational from April to June, 1996 after the launch of ERS-2. ERS-1 has outlived its planned operational life and was deactivated after the tandem mission. Currently, only ERS-2 remains in active operation.
ERS-1,2 Orbit
Sensors
ERS SAR Instrument Characteristics
Link to: ESA Earthnet (http://earth.esa.int/).  Back to Main Index Back to Main Index
|